🍃Docker Environment
A Docker environment is also a virtual environment, but unlike Python virtual environments, which are typically used locally, Docker makes your project portable across different platforms. As a result, Docker has become increasingly popular for production deployment.

An Example Project
This is a simple example to show the basic strusture of a python project that can be deployed to docker environment.
The core logic is stored in folder "core". In this example, it's just loading the data stored in folder "core", and print out the shape of the data.
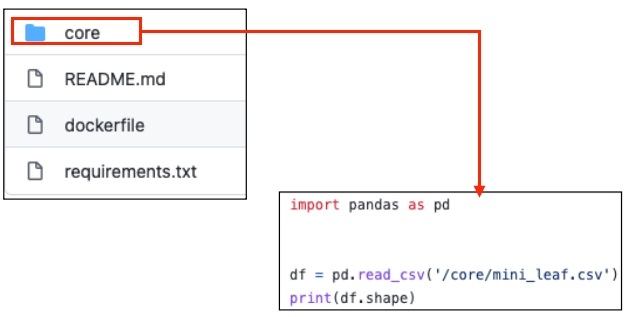
The key element is the dockerfile! The dockerfile contains all the instructions to build the docker image.

In the dockerfile below:
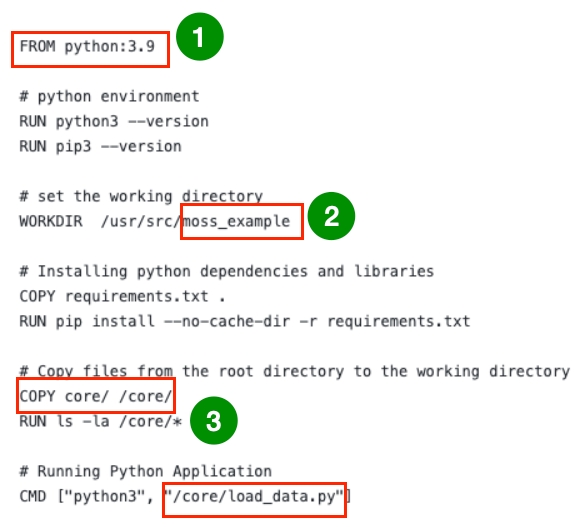
You need to specify the python version needed for your project, in this case, python3.9 was used.
WORKDIRindicates the project folder in the docker container, "/usr/src/" is often the root path, and "moss_example" will be the folder of this project in docker.

All the code in folder "core" will be copied to docker, under path "/usr/src/moss_example/core/". Suggest to have the source and destination folders share the same name in this copy command, so that your code can run both locally and run in docker.
🌻 Check Moss Example code repo >>
How to Setup Docker
Download and install docker desktop
To install docker on Windows: https://hub.docker.com/editions/community/docker-ce-desktop-windows
To install docker on Mac: https://hub.docker.com/editions/community/docker-ce-desktop-mac
Open a terminal,
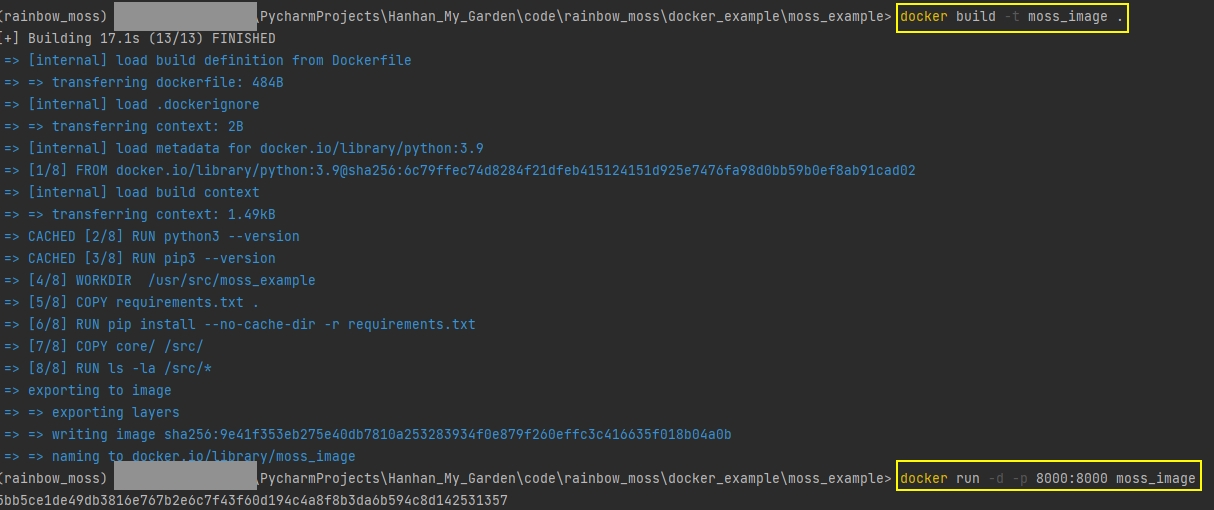
cdto your project folder where dockerfile locatesBuild the docker image by running
docker build -t [image_name] ., in this example, let's call our docker image as "moss_image"To run the docker image, type
docker run -d -p 8000:8000 [image_name]
The execution process looks as below, but you can't tell whether the core logic had been successfully executed.
To check Moss Example's output, you can open the Docker Desktop, click on the container that contains your image and check its log. If the execution failed, you can also find errors in this log.
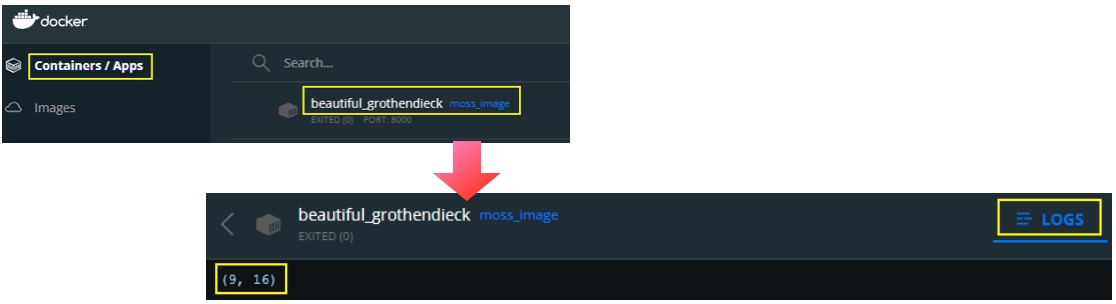
As shown above, Moss Example had been executed successfully. From here, you can develop more complex application running in the docker environment! 🎉
What's more, let's see some other commonly used commands:
The container names are randomly generated each time, you can type
docker ps -ato list all the contianers.docker stop [container_name]can stop a running container.docker system prunecan remove all the stopped containers and dangling images. Sometimes your docker environment will show weird errors, such as a certain dependency is not available even though everything is correct. Then this command can be useful to give your docker environment a fresh start by cleaning up those misleading items.
Last updated